I was involved in some recent work published in the Journal of Antibiotics (co-authors from Microbial Screening Technologies, Macquarie University, and Queensland Plant Pathology Herbarium) that describes the isolation, structure elucidation and antimicrobial activity of the talcarpones, which were isolated along with a known naphthazarin, aureoquinone. The paper is available here.
Interesting points:
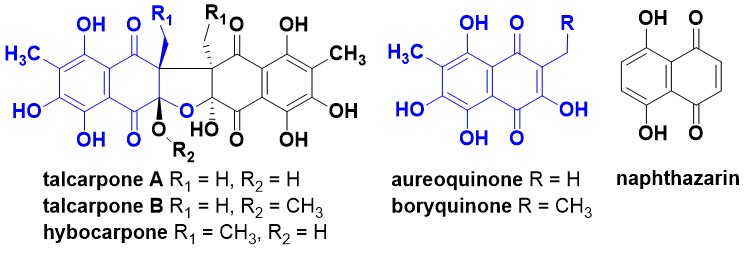
- These compounds were isolated from Talaromyces johnpittii sp. nov., which was named after John Ingram Pitt (1937–2022), an Australian food microbiologist and mycologist.
- The structures and relative stereochemistry of talcarpones A and B were secured by analysis of MS and NMR data. The absolute configuration of the talcarpones was tentatively assigned as 1 S,10 S,1′S,10′S using ECD calculations.
- The talcarpones and aureoquinone are homologues of hybocarpone and boryquinone, respectively. This is the first report of a homologue of hybocarpone, which had been previously reported from several fungal lichen symbionts. Although the relative configuration of hybocarpone was previously confirmed by X-ray crystallography and total syntheses, the absolute configuration was not assigned.
- Talcarpone A had MICs of 1.6 µg/mL against Candida albicans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and 12.5 µg/mL against Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus.
- Talcarpone B was shown to convert to talcarpone A in aqueous acetonitrile, which then partially converted to aureoquinone by an unknown mechanism.
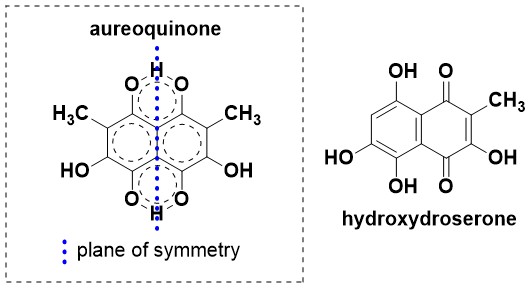
- The NMR data of aureoquinone showed that it contained a plane of symmetry. We hypothesised that facile intramolecular proton transfer mediated by proton tunnelling leads to very rapid tautomerisation and averaging of the quinone/quinol carbon resonances in aureoquinone, as has been reported for other symmetrical naphthazarins. Interesting, proton tunnelling is eliminated in asymmetrical environments such as hydroxydroserone.